Is 8 weeks of side-alternating WBV a safe & acceptable modality to improve functional performance in Multiple Sclerosis patients
Disabil Rehabil. 2011 Oct 12. School of Sport and Exercise, Massey University , Palmerston North , New Zealand.
Purpose: To examine whether an 8-week period of side-alternating whole-body vibration (WBV) exercise is an acceptable and effective exercise intervention to improve and maintain functional performance in multiple sclerosis people.
Methods: A total of 15 participants with MS (11 women [mean age 50.2 ± 6.9 years; body mass 65.7 ± 19.2 kg; height 165.3 ± 6.1 cm; EDSS 3.5 ± 0.9] and 4 males [mean age 50.5 ± 5.2 years; body mass 85.3 ± 16.0 kg; height 175.3 ± 3.2 cm; EDSS 3.4 ± 0.5]) were selected for this study. Quality of life, timed up-and-go, functional reach, standing balance and 10-m walk test were performed prior to and after 4 and 8 weeks of vibration exercise, and 2 weeks after cessation of vibration exercise.
Results: There was no evidence of vibration exercise producing any anxiety or discomfort. Compared with baseline measurements, the 10-m walk test showed significant improvements in 2, 8 and 10 m times at 8 week (p < 0.05) and 2 week post-vibration (p < 0.05). Timed up-and-go demonstrated a significant and positive time effect (p < 0.05). Standing balance showed significant improvements from baseline, at 4- (p < 0.05) and 2-weeks post-vibration (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: This is the first study to investigate side-alternating WBV as an exercise training modality for MS people. From an active MS population, this study has shown that WBV training not only improved the standing balance and walking time but there were also no adverse effects from using this modality.
PMID:21992525
SUMMARY STUDY: Patients with multiple sclerosis improved the SF36 questionnaire for quality of life, timed up and go test, functional reach test, standing balance and 10 m walk test. (see slide) The improvements persisted 2 weeks after the end of training. No adverse side effects were observed.
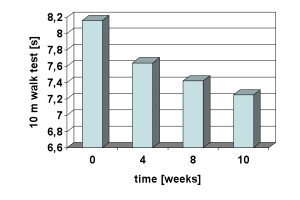 Compared with baseline measurements, the 10-m walk test showed significant improvements in 2, 8 and 10 m times at 8 week and 2 week post-vibration. Timed up-and-go demonstrated a significant and positive time effect. Standing balance showed significant improvements from baseline, at 4- and 2-weeks post-vibration
Compared with baseline measurements, the 10-m walk test showed significant improvements in 2, 8 and 10 m times at 8 week and 2 week post-vibration. Timed up-and-go demonstrated a significant and positive time effect. Standing balance showed significant improvements from baseline, at 4- and 2-weeks post-vibration
